Troubleshooting
If you are having a problem with Ditto, first follow this guide.
Obtaining and Analyzing the Debug Logs
To troubleshoot a peer-to-peer data sync issue, first determine the cause of the issue by obtaining and analyzing the database error and warning messages captured in the debug logs.
Setting the Logs to Debug Level
As demonstrated in the following snippet, obtain the database debug logs before Ditto is initialized so that any potential issues related to the file system access and authentication background tasks that run during initialization are tracked. You want to begin gathering logs before Ditto is initialized in order to capture any potential issues with those two background tasks.
DittoLogger.minimumLogLevel = .debuglet ditto = Ditto(identity: .onlinePlayground( appID: "REPLACE_ME_WITH_YOUR_APP_ID", token: "REPLACE_ME_WITH_YOUR_PLAYGROUND_TOKEN"))do { try ditto.startSync()} catch (let err) { print(err.localizedDescription)}Authentication success
For OnlinePlayground and onlineWithAuthentication identities, the first thing that Ditto needs to do is authenticate to the Big Peer.
Confirm that all devices share the same AppID by verifying that the app_id log line contains your AppID:
Ditto::new_from_uninit_ditto; app_id = 22389e28-9590-4cbf-b683-b3ac5ab2269e; site_id = 13769592724050309105; history_tracking = Disabled; presence_broadcast_targets = SmallPeersOnlyOnce confirmed, verify that authentication was successful.
AuthClient: authentication request succeededOnce authentication is successful, client re-authentication does not occur until the device's local certificate expires, as indicated by the following:
AuthClient: refreshing token in 302399 secondswarning
Incorrect APP ID
If the 'app_id' is incorrect, the following displays in the debug logs:
AuthClient: failed to get JSON for auth response; e = reqwest::Error { kind: Decode, source: Error("expected value", line: 1, column: 1) warning
Incorrect playground token
AuthClient: No valid Web token present. Can not request certificate.AuthClient: failed to obtain a certificate ValueNotFoundSee if the following fixes your issue:
- Log in to the Portal
- Go to your App.
- Copy the portal playground token and use it in your Ditto initialization.
warning
Outdated certificate
[DEBUG] 2023-08-03T17:36:35.046Z: failed to connect to peer; error = Connect failed because a TLS stream couldn't be established: invalid peer certificate contents: invalid peer certificate: UnknownIssuer; remote_peer = MulticastRemotePeer(id: 10, announce Q2RLCGEYdpLwjFditto)Your device's locally cached certificate is invalid. The device needs to call ditto.auth.logout() and reconnect to the Internet to get a new certificate. Alternatively, you can clear the local cache by reinstalling the mobile application or clearing the local persistence directory.
Syncing With the Big Peer
A small peer syncronizes with the Big Peer using a WebSocket connection.
The debug logs will tell you each step to create a successful WebSocket connection to the big peer.
First, the peer will discover the big peer and you'll see a Discovered event.
peer_event = Discovered(WebsocketClientPeer(WebsocketClientRemotePeer { id: 4, transport_id: 3, local_announce: LocalAnnounceData { outer_protocol_version: 50, os: Generic, network_id: 2383820004, query_overlap_group: None, device_name: "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537" }, connect_address: "wss://22389e28-9590-4cbf-b683-b3ac5ab2269e.cloud.ditto.live", routing_hint: RoutingHint(0), condition_sender: UnboundedSender { chan: Tx { inner: Chan { tx: Tx { block_tail: 0x242120, tail_position: 0 }, semaphore: Semaphore(0), rx_waker: AtomicWaker, tx_count: 2, rx_fields: "..." } } } }))If the WebSocket connection that links the Small Peer to the Big Peer is
successful, the debug logs contain the ConnectionEstablished event:
peer_event = ConnectionEstablished(PeerConnection { id: 4, connection_type: WsClient, remote_announce: Announce { outer_protocol_version: Some('2'), os: Some(Linux), network_id: Some(1356909299), query_overlap_group: None, device_name: Some("Ditto Cloud") }, remote_peer_id: SiteIdAndPubKey([...])warning
Corrupted certificate?
If your certificate chain is corrupted, you will see the following.
Connect failed because the underlying websocket transport reported an error: TLS error: webpki error: UnsupportedCriticalExtensioTo fix this, please try to reset your certificate chain. On MacOS, open the Keychain Acess application and navigate to the settings, and click "Reset default keychains..."
Keychain.app > Settings > Reset Default KeychainsYou will then see that the underlying physical replication session has been
started with phy started.
The pkSOME_BYTES identifer displays the public key to the Big Peer instance that a Small Peer WebSocket connection has temporary sync access.
Note that the following snippet is merely an example; the pkSOME_BYTES identifer is not a guaranteed static variable.
phy started; remote = pkAocCgkMCh0wD6Y83qm2UHtiN6264Jivvimg6xdR778ODaKODFKwOnce temporary remote access is authorized, the following debug log message appears to indicate that the Small Peer (client) WebSocket connection to the Big Peer (cloud server) is successful:
VirtConnElectedNewConn { new_conn: Some((4, WsClient)), old_conn: None }Permissions and Subscriptions
For the Small Peer to have an active subscription to read and write to other peers, it must first be authorized access by a Big Peer. If the Small Peer does not have permissions to access database replication, it cannot subscribe to its collections to read and write.
Permissions
Given this, before you check the Small Peer's active read-write subscriptions, confirm that the Small Peer has permissions to access the database.
local permission: Permission { read: PermissionRules { everything: true, queries_by_collection: {} }, write: PermissionRules { everything: true, queries_by_collection: {} } }, remote permission: Permission { read: PermissionRules { everything: true, queries_by_collection: {} }, write: PermissionRules { everything: true, queries_by_collection: {} } }Local permissions refer to the current peer that is running on the device.
Once the peer is authorized, it will begin to print the active subscriptions. Ditto will print the active subscriptions every time the sync engine wakes up. This includes a local write to the database or a sync event from another peer writing to their local database.
You will want to verify that these permissions are correct and what you expect. A peer cannot subscribe to a collection if it does not have read permission.
The default Big Peer remote permission to access a connected Small Peer local database replication to read and write is as follows:
write: { everything: true, queries_by_collection: {} }read: { everything: true, queries_by_collection: {} }Subscriptions
Now that default permissions are verified, confirm that the Big Peer is connected to a Small Peer and the local-to-global database replication task is running.
Ditto prints a list of all the queries that the peer is currently subscribed to.
local subscription: Subscription { everything: false, queries: {"__presence": {Query { expr: "_id != '13407763363308666127' && v == 3 && t > 1682717143093", order_by: [], limit: None, offset: None }}, "tasks": {Query { expr: "isDeleted == false", order_by: [], limit: None, offset: None }}} }, remote subscription: Subscription { everything: true, queries: {} }By default, each peer includes some internal subscriptions, which are denoted using
a double underscore (__) before the collection name; for example, the following default internal __presence subscription:
{"__presence": { expr: "_id != '13407763363308666127' && v == 3 && t > 1682717143093", order_by: [], limit: None, offset: None }}You will also see a list of remote subscriptions. The big peer subscribes to everything, so you will see the following line which references the big peer:
remote subscription: Subscription { everything: true, queries: {} }If there are any application-level subscriptions, they will be listed by collection. For instance, if a Small Peer that subscribes to all tasks that are not deleted, the following appears:
"tasks": {Query { expr: "isDeleted == false", order_by: [], limit: None, offset: None }}} If a subscription changes, the following appears:
Application: notifying a local subscription changeIf you have problems with subscriptions or permssions, you can try the operations with global read and write permission to verify that sync succeeds in this case. You can do this by using an OnlinePlayground identity, which defaults to global read and write permissions.
warning
Query Parsing Error?
ParseError can be printed in the debug logs when there is a problem with your
query. For example, if you create a subscription in Swift that is the empty
string, you will see a ParseError in the logs.
ditto.store.collection("myCollection").find("").subscribe() // -> ParseErrorWrites
If a Write is made to the local database, the following debugging messages appear:
Write txn committed; txn_id = 40; originator = UserNotifying a database change; transaction = 40Once a Write is made to the local database, Ditto re-prints the active subscriptions and permissions to access the debug log, as demonstrated in the previous snippet.
Next, the Small Peer creates the "update file." Annotated in the debug logs as follows, the update file provides the status of the data update and, using the pkA and pkB identifiers, indicates the two peers involved in the data exchange.
Creating a sending update, sending_update_path = "pkA/pkB/sending_update"Once the local peer finishes creating the update file, the following appears to indicate that the update file is complete and the local peer is ready to send the new update to the remote peer. Note that at this time the local Write has yet to be synchronized across all connected peers.
update creation done; since_index = 40; new_update_created = true; num_docs = 1; elapsed = 908us 708nsIf the local peer has received the update, all connected peers are synchronized, and the local database replication process is complete, the following appears:
No next update chunk to send - setting is_ready to falseNo message to sendDid your device connect to the internet?
OnlinePlayground applications must connect to the Big Peer first
before going offline. Read more about online playground.
Do you have a firewall or proxy enabled that is blocking Ditto's connection to the Big Peer?
A proxy may either either block connections or cause errors in the log by substituting its own
TLS certificate: invalid certificate: UnknownIssuer. If you see this log message you will either
need to get Ditto unblocked or add the CA certificate to the Small Peer's trusted certificate store.
Verify that you can reach the following endpoints. You should see the output exactly as written below:
> nc -v MY_APP_ID.cloud.ditto.live 443Connection to MY_APP_ID.cloud.ditto.live port 443 [tcp/https] succeeded!^C> curl -i https://MY_APP_ID.cloud.ditto.live/_ditto/auth/loginHTTP/1.1 405 Method Not AllowedDate: Fri, 30 Sep 2022 02:03:36 GMTContent-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8Content-Length: 23Connection: keep-aliveAccess-Control-Allow-Origin: *Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: trueAccess-Control-Allow-Methods: GET, PUT, POST, DELETE, PATCH, OPTIONSAccess-Control-Allow-Headers: X-DITTO-ENSURE-INSERT,X-HYDRA-ENSURE-INSERT,X-DITTO-CLIENT-ID,X-HYDRA-CLIENT-ID,Accept,Referer,Keep-Alive,User-Agent,X-Requested-With,If-Modified-Since,Cache-Control,Content-Type,Authorization,X-Forwarded-ForAccess-Control-Max-Age: 1728000
HTTP method not allowed% If this test passes, next check to see if WebSockets are blocked on your machine. Some corporate networks, firewalls, or proxies block the HTTP upgrade packet that tells the WebSocket server to keep the connection alive. Check with your IT administrator to see if your computer is configured to block WebSocket connections.
Online with Authentication
Did you follow the tutorial? The tutorial is your best guide for implementing this correctly. See the code on GitHub for a complete working example.
info
Common mistakes
- Send a POST request with a JSON stringified body to your server to ensure that the AWS-hosted Big Peer servers located in U.S. regions successfully send POST requests to your authentication server.
authenticationExpiringSoonandauthenticationRequiredboth need to be implemented according to the sample code.- Since callback objects are only invoked when Ditto initializes and the client authentication certificate expires, do not create subscriptions inside callbacks.
- Keep a strong reference to the AuthClient for the duration of the Ditto object, otherwise the auth handler will become garbage collected at an inappropriate time.
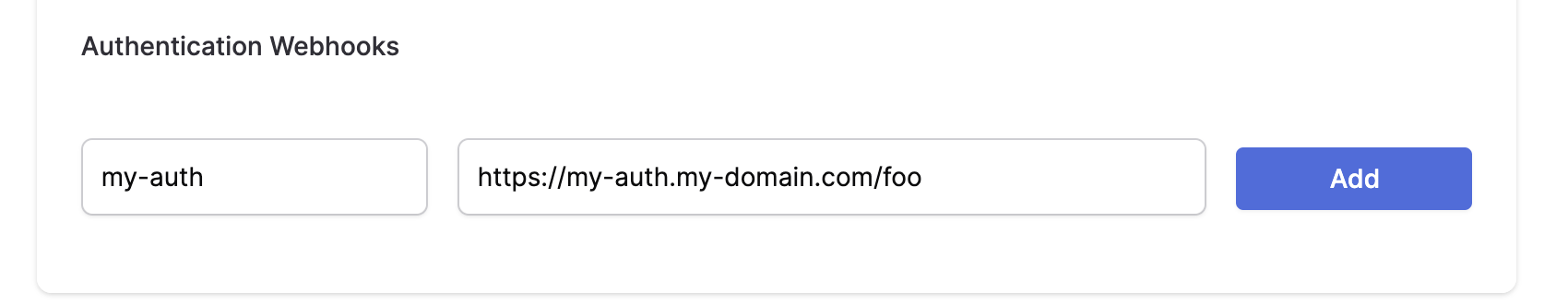
Verify that your webhook provider name is correctly copied in the Ditto portal.
The provider name given to the Ditto Client must match a provider name in the Portal (e.g., my-auth).
Is your AuthClient becoming garbage collected?
Ensure that you keep a reference to the AuthClient in scope for the duration that Ditto is also active. You should attach the dittoAuth variable to the object so it does not get garbage collected.
For example:
namespace Sync { public class DittoClient { private Ditto ditto;+ private DittoAuthDelegate dittoAuthDelegate;
public DittoClient(string appId, string id, string jwt) {+ dittoAuthDelegate = new DittoAuthDelegate(id, jwt); ditto = new Ditto(identity); } ... }}Bluetooth
- Turn Use Location on
- Turn Bluetooth Scanning on
- Are permissions set correctly? See installation.
- Go to your OS-level permissions for Bluetooth and clear the app permissions for your application.
- Delete the app, install it again, and open it. Does it ask for Bluetooth permissions?
- Android only: are you calling
ditto.refreshPermissions()?
Apple Wireless Direct Link, P2P-Wifi, Wifi Aware
- Are permissions set correctly? See installation.
- Go to your OS-level permissions and clear the app permissions for your application.
- Delete the app, install it again, and open it. Does it ask for location permissions?
- If you are using a custom
TransportConfig, make sure you have enabled all peer-to-peer transports usingenableAllPeerToPeer().
Local Area Network (LAN)
- Are permissions set correctly? See installation.
- Are both devices connected to the same WiFi network?
- Check your router settings and see the LAN troubleshooting guide.
- If your device has VPN enabled, then peers can fail to communicate. Ensure that your VPN supports UDP multicasting.
Synchronization seems slow, or comes to a halt over time
- Ensure that you are only creating a fixed number of live queries, with a smaller amount of data. Do not use
findAll()because you can sync more data than the small peer can reasonably handle. - Evict irrelevant data. You can evict all irrelevant once per day Read more here.
- Turn off verbose logging. Verbose logging can slow down replication considerably, especially with thousands of documents. Hence, it could look like that sync is stalling, but that can be indistinguishable from the logging mechanism slowing down ditto because it is trying to write too many lines.
- Look at the size of your ditto directory. Is it very large? Large databases will be slower. Try to query less data.
App is using too much memory, why?
Use profiling tools for your platform to better understand where the memory leak may be occurring.
A common issue we see in reactive apps is a failure to dispose of resources as
conditions change. Your app could create a large accumulation of publishers that
infinitely grow. Every liveQuery and subscription in ditto must be explicitly
stopped using the stop or cancel API. See snycing data for more information.
Debugging Blocked Transactions
info
💡 This section only discusses blocked transactions on native platforms (e.g. iOS, Android, Windows, Linux). Ditto in web browsers operates sufficiently differently and isn’t covered here.
Blocked write transactions will automatically retry until they succeed. A blocked write transaction will never crash. Howewever, blocked write transactions are a common cause for poor database performance. Long running blocks are generally bad since they mean that nothing else can be writing to the database during this time. This could manifest itself as one of many problems:
- Unresponsive UI: an interaction might try to update a document, but is blocked by an existing write transaction
- Slow sync: new updates cannot be integrated into the store, since they’re blocked by another write transaction
A blocked write transaction can hint that something is wrong with the application code, or at a deeper level in Ditto. This page contains some tips & tricks to help understand the situation.
The process of unblocking is automatic and you don’t need to write any code to handle this. However, you can drastically reduce the chance of blocking transactions by making sure a device is only syncing the data it really needs.
What is a “blocked” transaction?
At any given time, there can be only one write transaction. Any subsequent attempts to open another write transaction will become blocked until the existing write transaction finishes.
Read vs. Write Transactions
Read transactions operate differently to write transactions.
Read transactions cannot be blocked and can run in parallel with write transactions. Read transactions don’t block each other, don’t block write transactions, and aren’t blocked by write transactions.
If a write transaction is blocked, Ditto will log a message with increasing severity every 10s.
| Time (t) a transaction has been blocked | Log Level |
|---|---|
| t ≤ 30s | DEBUG |
| 31s < t ≤ 120s | WARN |
| 120s < t | ERROR |
To see these logs in the database, it’s important to have a minimum log level set. Transactions that are blocked for over 2 minutes should always be visible in the logs.
If INFO level is used, then INFO, WARN, and ERROR messages will all be
included in the logs. This means any write transactions blocking for more than
30s should always be visible in the logs.
Reading the Logs
If a write transaction is blocked, the device logs will look something like the following. In this example we can see a write transaction was blocked for a total of 150s (or 2.5 minutes).
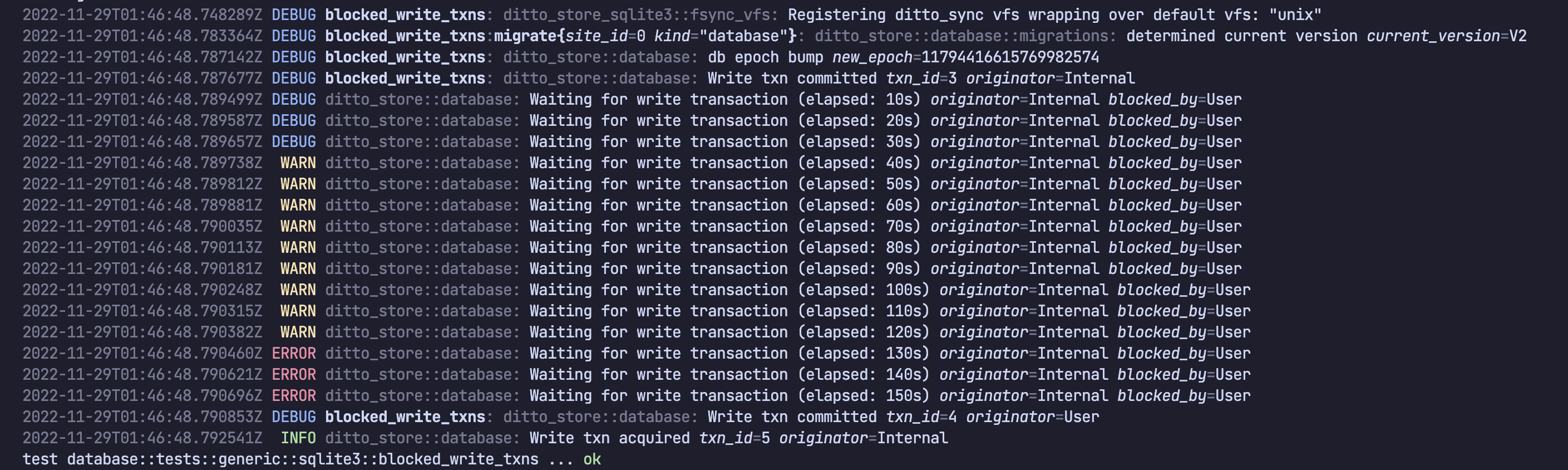
As time progressed, Ditto complained more and more loudly (starting with DEBUG
logs before eventually logging at ERROR level). Eventually the existing
transaction finished and blocked transaction was was able to proceed.
The write transaction which was blocked was for a Ditto internal component. This is identified by
“originator=Internal”.
The existing, long-running write transaction which was causing the block was a
user call in the public SDK. This is identified by
“blocked_by=User”. So a user-level write transaction is blocking some internal
workload. This is not necessarily a problem, as the internal system will catch up eventually.
Originators
The three values you’ll see for originator and blocked_by are:
| Originator / Blocked By | Description |
|---|---|
| “User" | Any user-level API which modifies data. |
| “Internal" | An internal job (presence data, DB maintenance, etc.). |
| “Replication" | Updating the store with data received via replication. |
Causes of Blocked Transactions
This section presents a few examples blocked transaction scenarios, how they would appear in logs, and what they might mean.
User blocks User
An application might block its own write transactions by performing multiple writes at the same time in different places. If one is slow (perhaps it does too much work, or perhaps it reaches out to external APIs, etc.) then the other write transactions will block until it finishes.
// Thread/Queue 1 (starts first):{ // Somewhere in the app, a long running write transaction exists ditto.store["people"].findByID(docID).update { mutableDoc in // Most update tasks are quick, but a developer might // doing something slow within the update block: let apiData = getDataFromASlowExternalAPICall() // <-- !!!! mutableDoc?["age"] = apiData.age mutableDoc?["ownedCars"].set(DittoCounter()) mutableDoc?["ownedCars"].counter?.increment(by: apiData.count) }}
// Thread/Queue 2 (starts second):{ // Somewhere else in the app, concurrently (e.g. background thread or queue) // another write transaction tries to update a document. // // This will block until the "people" update block above completes. let docID = try! ditto.store["settings"].upsert([ "_id": "abc123", "preference": 31, ])}In logs, this scenario will look like the following:
LOG_LEVEL: Waiting for write transaction (elapsed: XXs), originator=User blocked_by=User
Note that “User” is blocking “User”. This could be temporary, but it could also be a deadlock which is much worse. See below.
User deadlocks User
// Start a write transaction:ditto.store["people"].findByID(docID).update { mutableDoc in // Start a write transaction _within_ a write transacton. // !! Deadlocks !! let docID = try! ditto.store["settings"].upsert([ "_id": "abc123", "preference": 31, ])
// ...}You cannot start a write transaction within a write transaction. The result will be a deadlock which never resolves itself. This might manifest itself in the logs as:
LOG_LEVEL: Waiting for write transaction (elapsed: XXs), originator=User blocked_by=User
Note that User blocking User doesn’t necessarily mean a deadlock. It might
merely be a long running write transaction and this situation might be expected
depending on the task. However, if the transaction never unblocks and the log
messages at ERROR level continue forever - you have a strong indication that
there’s a deadlock and should investigate the application code.
Replication blocks User
// Somewhere in the app, a simple enough user write transaction is happening.// There's no other user write transaction happening concurrently in the// app, yet the update seems blocked or slow and UI might seems slugglish// or unresponsive.let docID = try! ditto.store["settings"].upsert([ "_id": "abc123", "preference": 31,])From the application code, it might not be obvious what the problem is. By looking in the logs, you might get a hint. For instance:
LOG_LEVEL: Waiting for write transaction (elapsed: XXs), originator=User blocked_by=Replication
Here we can see that replication is blocking our user’s write transaction. This might happen if we’ve just received a large amount of sync data from another peer. Most commonly, happens during initial sync (either with the Big Peer, or joining a mesh for the first time, or re-joining a mesh after an extended period away).
This scenario is something to be aware of, but will resolve itself automatically once the sync is complete. The user transaction will eventually unblock and continue when replication has finished updating the store.
Replication blocks Replication
If you see the following in logs, it’s an indication that one replication session with a remote peer is blocking another:
LOG_LEVEL: Waiting for write transaction (elapsed: XXs), originator=Replication blocked_by=Replication
This can happen when the device has received large amounts of data from multiple peers simultaneously and must update the database with the changes it received from each. Ditto can only update the database with sync data from remote peers one at a time, so the other updates must wait their turn.
This scenario is most likely to happen during a large initial sync - either with the Big Peer at the same time as with nearby devices, or just with multiple nearby devices when joining a mesh for the first time (or re-joining after an extended period away).
This scenario is something to be aware of, but will resolve itself automatically once the sync is complete. You can drastically reduce the chance of this type of blocking transaction by making sure each device is only syncing the data it really needs.
User or Replication blocks Internal
A long running write transaction might block an internal job. This scenario will be the least obvious to spot and it might not be obvious that it’s happening at all. It’s also the least likely to cause actual problems.
// Somewhere in the app, a long running write transaction existsditto.store["people"].findByID(docID).update { mutableDoc in // Most update tasks are quick, but you might // doing something slow within the update block let apiData = getDataFromASlowExternalAPICall() // <-- !!!!
mutableDoc?["age"] = apiData.age mutableDoc?["ownedCars"].set(DittoCounter()) mutableDoc?["ownedCars"].counter?.increment(by: apiData.count)}In logs, you might see the following:
LOG_LEVEL: Waiting for write transaction (elapsed: XXs), originator=Internal blocked_by=User
or:
LOG_LEVEL: Waiting for write transaction (elapsed: XXs), originator=Internal blocked_by=Replication
That is, something is blocking Internal.
If you observe slow and unreliable Ditto Bus connections, an inaccurate presence viewer, or slow and unreliable multi-hop data replication, a Write transaction may be preventing the internal mesh presence component to persist data in regular 30-second intervals.
Once the blocking Write transaction is complete, the observed issue should resolve itself automatically.
Still stuck?
If you continue to have problems, please email us at support@ditto.live or login to your Ditto account to chat with the support bot located in the lower right corner of your screen. An engineer will reach out to you shortly.